Para cambiar el origen de nuestro repositorio git, debemos usar el comando git remote add, que nos permitirá agregar un nuevo repositorio desde el cual realizar las operaciones de clonación, pull y push. Ahora necesitamos saber cómo agregar un nuevo control remoto a su repositorio de Git.
El comando git remote add contiene dos argumentos que debemos conocer:
- Un nombre remoto único, por ejemplo, «my_software_repo_git»
- Una URL remota, que puedes encontrar en el botón de clonación de tu repositorio de gitlab.
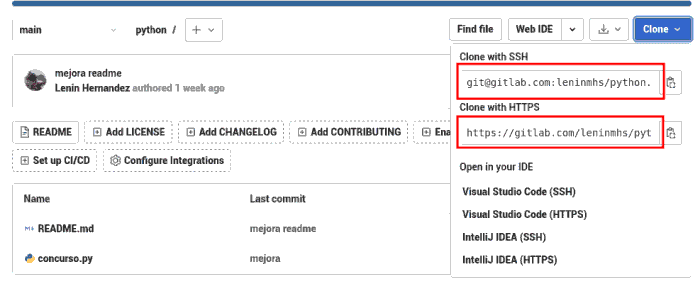
Para agregar un nuevo repositorio remoto, debe usar el comando git remoto add en la terminal, dentro del directorio en el que está almacenado su repositorio.
cd sistemaxyz/
git remote -v
git remote set-url origin [email protected]:leninmhs/sistemaxyz.git
Para cambiar origen del repositorio #GIT Ideal por ejemplo si clonan un proyecto vía https pero al cabo de los días ya no quieren seguir colocando la clave (ssh-key) para cada operación
cd sistemaxyz/
git remote -v git remote set-url origin [email protected]:leninmhs/sistemaxyz.git
El origen git remoto set-url reemplazará su repositorio basado en https con uno basado en ssh, en el ejemplo usando gitlab. Si no tiene la clave ssh creada, créela con ssh-keygen, copie el valor de: .ssh/id_rsa.pub (for linux users) y ponlo en tu cuenta de gitlab en -> Preferences -> SSH keys
Con el comando git remote -v podemos ver los orígenes remotos que tiene tu repositorio GIT



